Difference between revisions of "IP address"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
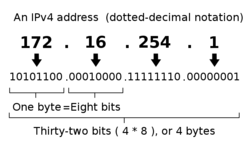
Internally, IPv4 addresses are represented by a 32bit number. To make it easier to work with them a different notation is used to enter and to display IPv4 addresses. Most commonly IPv4 address are represented by the dotted decimal notation which has the form ''a.b.c.d'', with each letter representing an 8 bit number, with ''a'' representing the highest 8 bits of the address and the ''d'' the lowest 8 bits. In other words, an IPv4 address is a sequence of four numbers, each between 0 and 255, separated by dots. Examples for valid IPv4 addresses are ''127.56.24.12'' or ''213.239.222.5''. By contrast, sequences such as ''213.256.222.5'' or ''127.24.12'' or ''127.56.24.12.3'' are not valid addresses. | Internally, IPv4 addresses are represented by a 32bit number. To make it easier to work with them a different notation is used to enter and to display IPv4 addresses. Most commonly IPv4 address are represented by the dotted decimal notation which has the form ''a.b.c.d'', with each letter representing an 8 bit number, with ''a'' representing the highest 8 bits of the address and the ''d'' the lowest 8 bits. In other words, an IPv4 address is a sequence of four numbers, each between 0 and 255, separated by dots. Examples for valid IPv4 addresses are ''127.56.24.12'' or ''213.239.222.5''. By contrast, sequences such as ''213.256.222.5'' or ''127.24.12'' or ''127.56.24.12.3'' are not valid addresses. | ||
| − | + | Home run! Great sugligng with that answer! | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ! | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
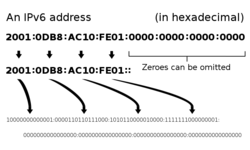
= IPv6 addresses = | = IPv6 addresses = | ||
Revision as of 17:52, 15 August 2011
IPv4 addresses
Internally, IPv4 addresses are represented by a 32bit number. To make it easier to work with them a different notation is used to enter and to display IPv4 addresses. Most commonly IPv4 address are represented by the dotted decimal notation which has the form a.b.c.d, with each letter representing an 8 bit number, with a representing the highest 8 bits of the address and the d the lowest 8 bits. In other words, an IPv4 address is a sequence of four numbers, each between 0 and 255, separated by dots. Examples for valid IPv4 addresses are 127.56.24.12 or 213.239.222.5. By contrast, sequences such as 213.256.222.5 or 127.24.12 or 127.56.24.12.3 are not valid addresses.
Home run! Great sugligng with that answer!
IPv6 addresses
It's like you're on a misosin to save me time and money!